About five earthquakes of magnitude 5.0 or higher on the Ritcher scale occur on our planet every day. Researchers from the IISc, Bengaluru, King Saud University, Saudi Arabia, and BARC, Mumbai, have reported a method to better identify building sites with soil that could be susceptible to damage from earthquakes.
IISc
We all remember learning to read—at first, we were taught to read each letter or sound at a time laboriously. Eventually, we picked up reading entire words and sentences effortlessly. But, it is not yet clear as to what changes in our brain when we learn to read. In a recent study, researchers at the Indian Institute of Science, Bengaluru, have identified these changes in the brain changes that help in visually processing the words and helps us to read efficiently. The study was published in the journal Psychological Science and was funded by the Department of Biotechnology-Indian Institute of Science (IISc) Partnership Programme and the Wellcome Trust/DBT India Alliance.
Researchers from the Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore; Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology, Pune; and Florida State University, USA; have mathematically computed a multidecadal variability in the Indian summer monsoon rainfall and the global sea surface temperature. They have established that Indian monsoon rainfall exhibits a 67-year oscillation and is closely linked to the sea surface temperature cycle, which also shows a similar 67-year swing. The study also shows that 80% of all droughts have occurred in the rainfall cycle’s ‘negative phase’, associated with a below-average rainfall; whereas 60% of all floods have occurred in the positive phase, marked with above-average precipitation. Their findings have been published in the Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society.
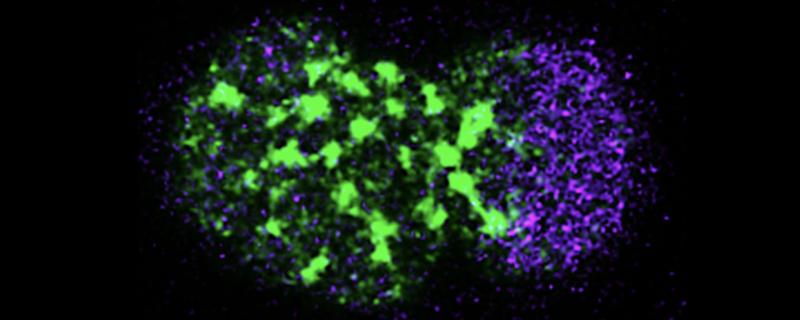
Several interacting molecular and biochemical processes are vital to establishing cell polarity. In a recent study, researchers at the Indian Institute of Science, Bengaluru, studied some of these signals in the centrosome—an organelle in the cell responsible for cellular organisation—of a single-cell embryo.
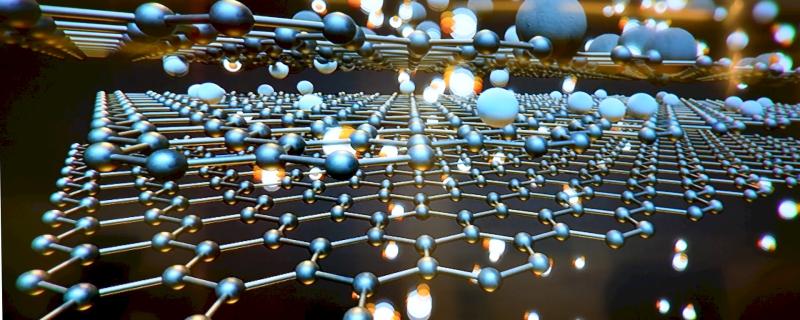
Graphene, a sheet-like form of carbon, has been hailed as a wonder material owing to its many promising applications in electronics, drug delivery and more. In a recent study, a team of scientists from India and the USA, led by Prof Srinivasan Raghavan and Prof Rudra Pratap from the Indian Institute of Science (IISc), Bengaluru, has paved the way for new applications of graphene by intentionally varying the defects formed during its production.
Our genetic material is a big molecule of DNA or deoxyribonucleic acid, whose structure is a double-stranded wound-up helix. It contains specific instructions that run a living cell, and these instructions are written on the strands. When cells divide, the DNA replicates too. In this process, the contents of the strands are read and copied carefully by unwinding the strands. But that's not as simple!
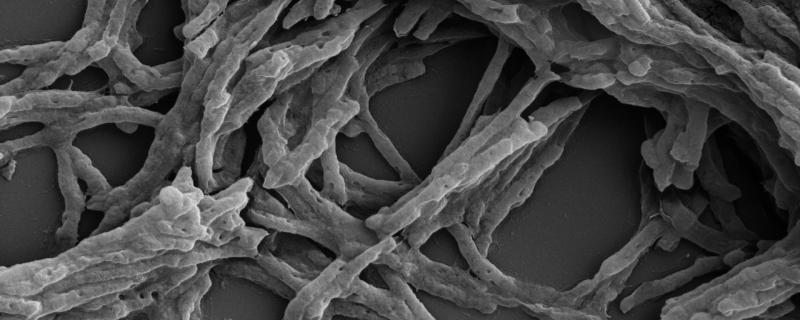
In 2018, around 1.5 million people died from tuberculosis (TB) — an infectious disease that mainly affects the lungs. A major obstacle in the clinical treatment of TB is the long therapy time required to clear the infection. An infected patient needs to take antibiotics for over 6 to 9 months to prevent a relapse — a duration so long that many discontinue their medications.
Imagine just switching on your lights and downloading a movie in a second. The world demands high-speed internet connectivity at a lower price. This increasing clamour for speed and bandwidth is opening up new avenues, and one such evolving domain is LiFi - a wireless technology that makes use of light-emitting diodes (LEDs) to transmit data. Light waves are 10,000 times denser than WiFi signals, so there is vast untapped potential here.
Study shows how paper wasps use the space in their nests to feed their larvae and fend off diseases.
The blackbuck is an antelope species native to the Indian subcontinent. Although the term 'antelope' is loosely used to refer to many ruminating ungulates, the blackbuck is the only animal that belongs to the genus named Antilope. True antelopes belong to one of the four genera—Gazella, Nanger, Eudorcas and Antilope. Scientists are still debating the evolutionary relationships between these members. In a recent study, researchers at the Indian Institute of Science, Bengaluru, have traced the evolutionary relationships of the blackbuck (Antilope cervicapra) using phylogenetics. The study was published in the journal Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution.