The Amazon river is the largest river system in the world, discharging huge volumes of fresh water into the ocean. Scientists from the Center for Atmospheric and Oceanic sciences have explored what would be the effect of the reduction in the Amazon river’s runoff into the ocean. The scientists demonstrate the wide ranging climatic changes that can occur if the river discharges lesser water into the Atlantic ocean.
Archives
A team, including scientists from University of California, Santa Barbara, USA and Indian Institute of Technology -Kanpur, have developed a new technique to reduce the amount of carbon dioxide produced while making hydrogen. The new method not only reduces the amount of greenhouse gases, but also allows for the reuse of carbon that is produced in the reaction.
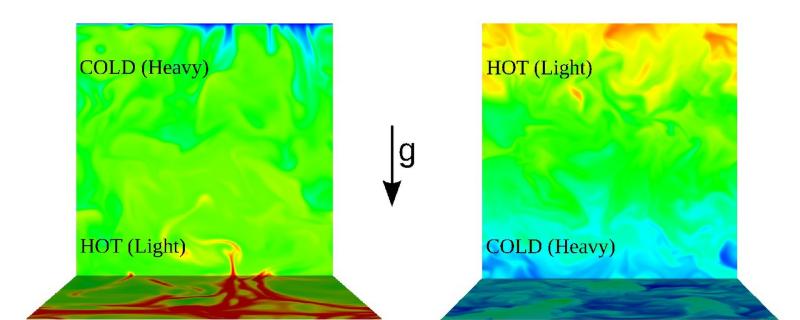
When energy is supplied to a fluid, it flows. As this energy is increased the flow becomes turbulent. If the energy is provided through heat, we see buoyancy driven turbulence, where the hotter fluid rises to the top and colder fluid moves to the bottom. A conjecture that explained such buoyancy driven turbulent flows may now be overturned. New insights gained in a study using one the world’s most powerful supercomputer could help better explain such flows.
In a first, scientists from Indian Institute of Technology Ropar (IIT RPR), Rupnagar, University of Edinburgh and Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur (IIT Kgp) have demonstrated a phenomenon called ‘inverse Marangoni effect’ using nanodroplets of pure water.
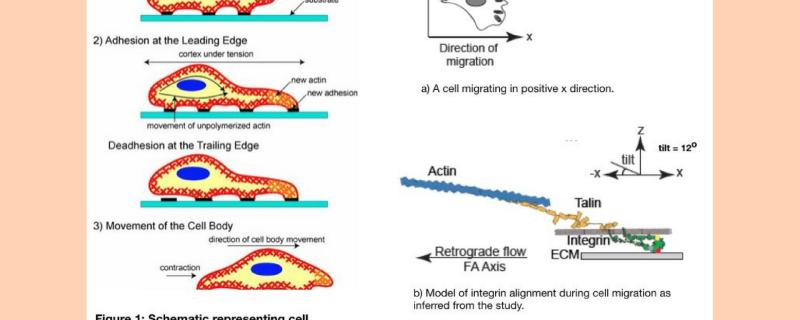
Many important process in the body require the movement of cells. From forming our fingers during the development of an embryo to healing wounds in adults, all are possible due to cell movement. But how does cell know in what direction it should move? A collaborative study from Marine Biological Laboratory (MBL), Woods Hole, USA comprising researchers from NCBS Bangalore, National Institutes of Health and Harvard Medical School, USA, find strong evidence for the ‘cytoskeletal force model’, which is one way of explaining how cells move.
Scientists from the National Institute of Plant Genome Research have identified a protein that helps bacteria consume fungi.
A galaxy supercluster is the largest known structure in the Universe, made of dozens of galaxy clusters, themselves containing thousands of galaxies. The Saraswati Supercluster, discovered this year by a team of Indian scientists, is the largest known galaxy cluster today. It extends over 650 million light years across and weighs more than 20 billion suns would. We caught up with Prof. Joydeep Bagchi, who led the team that discovered Saraswati Supercluster, for a chat about the importance and implications of the discovery.
When we think of diseases that come to us from animals, rabies and AIDS are the most common ones that pop into our heads. Rabies is one of the most common viral zoonotic infections. Some of the widely known facts about rabies are that it makes you a slobbering, aggressive madman, it’s acquired by the bite of an infected dog and that it kills you.
Scientists from the Indian Institute of Science Bangalore devise a computational model to study how cooperation evolves in natural systems - from cells to large mammals. The study finds mobility, which was largely ignored before, plays a key role in the evolution of cooperation. Understanding mobility of cells in a medium could help us understand better the spread of cancer.
Researchers from Washington University, St. Louis, USA surveyed Indian households to determine the ease of obtaining education and factors that hinder the process, in the country.