During the fag end of 2015, Chennai experienced severe floods resulting in the death of about 500 people and economic losses of about INR 50,000 crores. The flooding stranded the city and was termed a 'man-made disaster' resulting from irresponsible water management and rapid urbanisation. The northeast monsoon of the year left most parts of South India marooned, exposing how vulnerable our cities are to such catastrophes. That's when the Office of the Principal Scientific Advisor took a major initiative to develop a real-time, integrated, urban flood forecasting system that was non-existent in our country. Soon after, a team of scientists from various institutes across the country, swung into action to develop the first-ever expert system in India to forecast floods. In a recent study, published in the journal Current Science, the researchers shed light on the development of the automated flood forecasting expert system.
IIT Bombay
Study analyses what drives the choice of transport to shopping malls in Mumbai.
Study by Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, uses digital processing of archived satellite images to study the growth patterns in the Mumbai Metropolitan Region.
Bureaucracy and political interests hinder the implementation of the Forest Rights Act, finds study
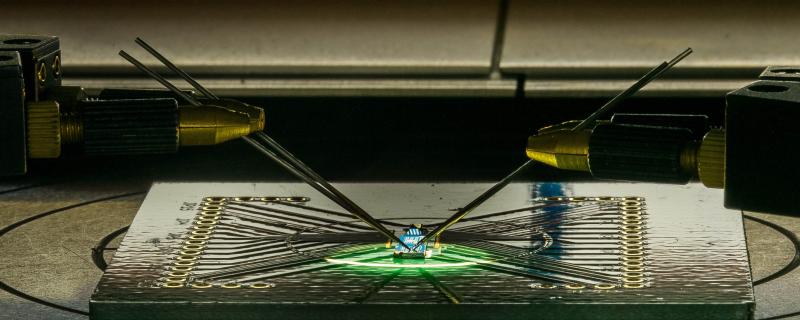
Researchers find a unique new technique to make stable, low-power graphene transistors
Researchers at IIT Bombay develop the country’s first indigenously designed and fabricated microprocessor.
Prof Subimal Ghosh, Professor at the Department of Civil Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology Bombay (IIT Bombay), has been awarded the Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Prize 2019 by the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR). This award recognises his significant contributions to our understanding of how land surface processes influence the Indian monsoon, as well as for improving regional monsoon simulations and predictions.
Researchers from IIT Bombay and Archaeological Survey of India, Aurangabad studied soil from the Lonar lake and found that the materials from the meteor had a significant impact on the native soil.
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder where the body does not produce or effectively use the hormone insulin, resulting in elevated levels of glucose in the blood. Monitoring the amount of blood glucose can aid effective diagnosis, treatment, and access to quality healthcare management to diabetic patients. One of the ways to monitor blood glucose is through commercially available biosensors. Although such a test can be done at home at any time, there is a growing need to have pain-free alternatives. Hence, researchers are exploring glucose biosensors that do not need so much blood and are reliable, accurate, biodegradable, biocompatible and user-friendly. In a recent study, published in the journal Scientific Reports, researchers at the Indian Institutes of Technology Indore and Bombay, have developed one such sensor.
Researchers from IIT Bombay, Microsoft India and Google Inc, develop a search system to extract meaningful data from live social media posts
![Inundation of Chennai by Kaitha Poo Manam [CC BY-SA 3.0] via Wikimedia Commons Fighting floods the 'expert' way](/sites/researchmatters/files/styles/large_front_800x320/public/chennai_flood.jpg?itok=EhgzFr0n)


![Davidvraju via WikiCommons [CC BY-SA 4.0] Bureaucracy and political interests hinder the implementation of the Forest Rights Act, finds study](/sites/researchmatters/files/styles/large_front_800x320/public/iitb_9.jpg?itok=79PwKoj8)