Scientists from the National Centre for Biological Sciences, Bangalore study what neurons are involved in the identification of bitter substances by fruit flies.
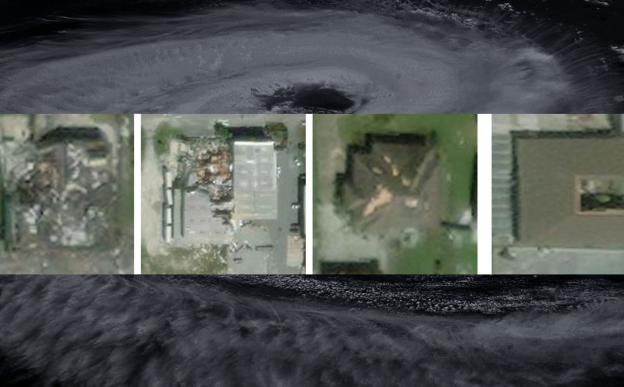
IIT Bombay’s new deep learning framework, named SpADANet, enhances damage classification accuracy using limited labels across multiple hurricanes.
Mumbai/