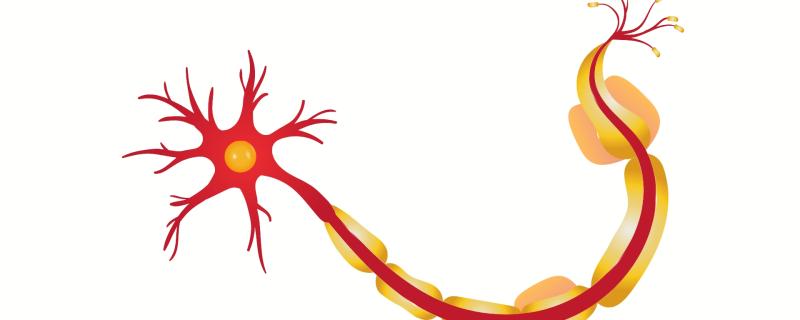
In a new study, the researchers from the Raman Research Institute (RRI), Bengaluru, in collaboration with researchers from France and Chile, provide us with an understanding of the physical forces that drive axonal beading and retraction. The findings could hold new insights on understanding neurodegeneration. The results of the study, funded by the Department of Science and Technology (DST), are published in the Biophysical Journal.
Despite successful bans on the veterinary drug diclofenac in Nepal and parts of India, a decade-long undercover investigation reveals that toxic alternatives like flunixin and nimesulide are rapidly replacing it, posing a renewed existential threat to the region’s critically endangered vulture populations.
Mumbai/





![Participants of the annual bat harvest in Nagaland, India, counting and bundling bats, which will be distributed to male members of the Bomrr clan for consumption [Image credit: Dr Zavei Hiese] On the edge: Bats in northeast India found to carry filoviruses that could spread to humans](/sites/researchmatters/files/styles/large_front_800x320/public/bats.jpg?itok=p7IVXnxl)