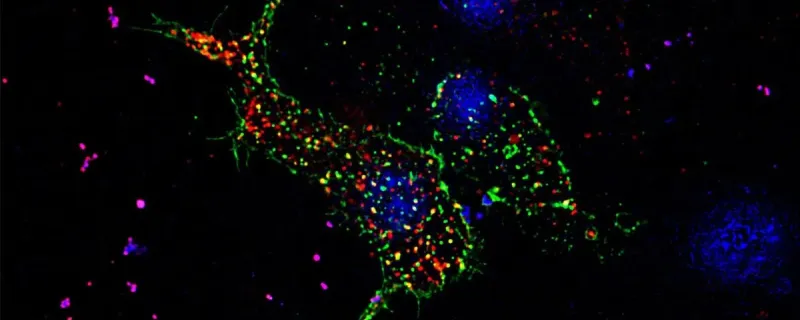
A recent study from the Indian Institute of Science (IISc) has shed light on how this glucose traffic management goes wrong in Type 2 Diabetes (T2D), offering exciting new possibilities for treatment.
A new review reveals that rising global temperatures, increased pollution, and extreme weather events are driving a global surge in eye diseases, disproportionately affecting vulnerable communities and challenging healthcare systems.
Roorkee/