The Andaman and Nicobar Islands are a group of islands and a Indian union territory situated 1200 kms from the easternmost boundary of the Indian peninsula. Although some distance from the mainland, scientists have now found evidence for the effects the islands and the surrounding Andaman sea have on the climate on the mainland. Using satellite data and computer simulations, the scientists have established the area as an important contributor to the Indian Monsoon and as one which requires further study.
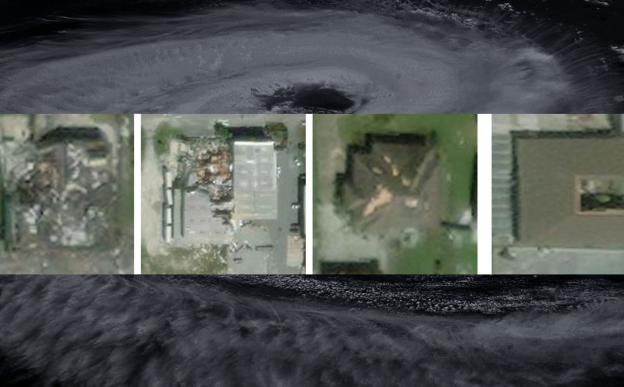
आयआयटी मुंबईद्वारे विकसित नवीन डीप-लर्निंग फ्रेमवर्क SpADANet (स्पाडानेट) मर्यादित लेबल्स वापरूनही अनेक चक्रीवादळांमधील संरचनात्मक नुकसान अधिक अचूकपणे वर्गीकृत करू शकते.
Mumbai/