প্ৰতি বছৰে অক্টোবৰ মাহৰ মাজ ভাগত নাগালেণ্ডৰ ব’মৰ (Bomrr) নামৰ জাতি এটাৰ লোক সকল মিমি গাওঁত থকা গুহা সমূহত একত্ৰিত হয়। বছৰেকীয়া এই বাদুলি চিকাৰৰ উৎসৱত প্ৰায় ৭০০০ ৰ পৰা ২৫০০০ টা বাদুলি হত্যা কৰা হয়। এই জাতিটোৰ লোক সকলে বিশ্বাস কৰে যে এই বাদুলিসমূহৰ কিছুমান ঔষধিক গুণ আছে যিয়ে ডায়েৰীয়া, দেহৰ বিষ ইত্যাদি নিৰ্মূল কৰিব পাৰে আৰু শক্তি বৃদ্ধি কৰে। কিন্তু এক শেহতীয়া অধ্
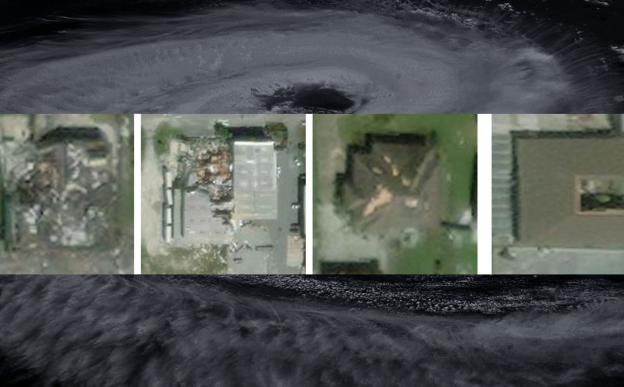
आईआईटी मुंबई द्वारा विकसित नया स्पाडानेट (SpADANet) नामक डीप लर्निंग फ्रेमवर्क सीमित लेबलों का उपयोग करते हुए कई, चक्रवातों में हुए हानि के वर्गीकरण की सटीकता को बढ़ाता है।
Mumbai/






![ಸಂಶೋಧನೆಯಲ್ಲಿ ಅಧ್ಯಯನ ಮಾಡಲಾದ ಮೂಳೆಯ ಅವಶೇಷಗಳು. [ಛಾಯಾ ಚಿತ್ರ ಕೃಪೆ : ವಸಂತ್ ಶಿಂಧೆ] ನಾವು ಭಾರತೀಯರು ಎಲ್ಲಿಂದ ಬಂದವರು?](/sites/researchmatters/files/styles/large_front_800x320/public/figure-2-skeletal_remains_-_vasant_shinde.jpg?itok=Yl6vOntA)

![निलांजन मुजुमदार via Wikimedia Commons [CC BY-SA 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0)] हवामान बदलांमुळे उद्भवणाऱ्या दुष्परिणामांना सामोरे जाताना](/sites/researchmatters/files/styles/large_front_800x320/public/iitb_8.jpg?itok=3C4vvgFi)
