A new study reveals how wastewater surveillance can track flu, RSV, and COVID-19 variants, offering a unique window into community health.
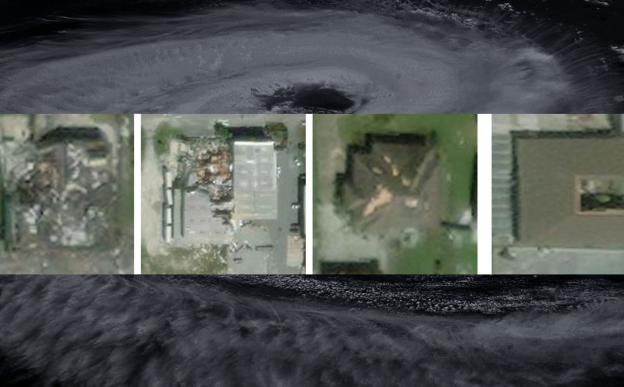
IIT Bombay’s new deep learning framework, named SpADANet, enhances damage classification accuracy using limited labels across multiple hurricanes.
Mumbai/