ZSI researchers have officially introduced the genus Anaplectoidea to India, describing two entirely new species and hinting at more undiscovered diversity within the country's rich ecosystems.
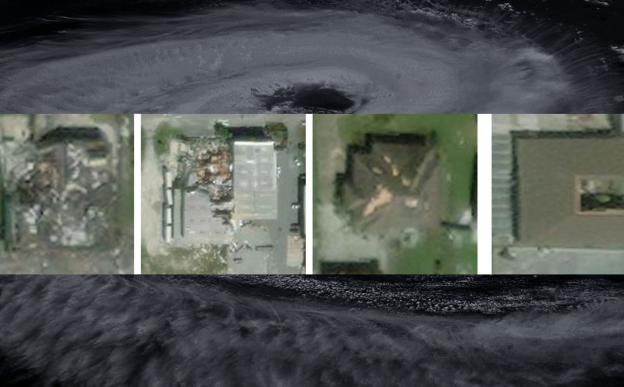
आयआयटी मुंबईद्वारे विकसित नवीन डीप-लर्निंग फ्रेमवर्क SpADANet (स्पाडानेट) मर्यादित लेबल्स वापरूनही अनेक चक्रीवादळांमधील संरचनात्मक नुकसान अधिक अचूकपणे वर्गीकृत करू शकते.
Mumbai/