In a study published in the journal The Lancet Oncology, the researchers collected and analyzed data from various published reports such as the Global WHO FCTC Implementation Progress Reports of 2012, 2014, 2016, 2018, WHO reports on global tobacco epidemic 2013, 2015 and 2017, Global Tobacco Surveillance System Data and the WHO-NCI Monograph. They examined the prevalence, trends and policy progress in smokeless tobacco control on the lines of the WHO FCTC guidelines.
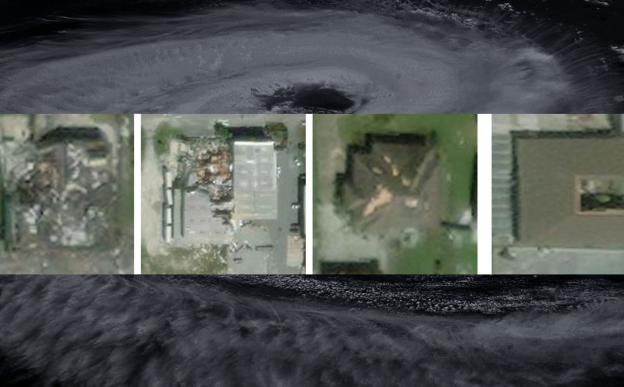
आयआयटी मुंबईद्वारे विकसित नवीन डीप-लर्निंग फ्रेमवर्क SpADANet (स्पाडानेट) मर्यादित लेबल्स वापरूनही अनेक चक्रीवादळांमधील संरचनात्मक नुकसान अधिक अचूकपणे वर्गीकृत करू शकते.
Mumbai/